Quick summary:
SaaS adoption in Canada is booming, but security and compliance are now business-critical.
- Compliance Laws: PIPEDA, provincial privacy acts, and upcoming Bill C-27/CPPA define strict data rules.
- Key Risks: Shadow IT, poor access controls, and cross-border data storage create major vulnerabilities.
- SMB Challenges: Limited resources make vendor certification tracking and audit readiness difficult.
- Best Practices: Audit SaaS tools, enforce RBAC + MFA/SSO, prioritize Canadian data centers, and automate monitoring.
- Clarro Advantage: Simplifies SaaS governance with centralized tracking, shadow IT detection, and compliance automation.
SaaS adoption across Canada is accelerating. In 2023, nearly 50% of Canadian businesses reported using cloud computing services, with SaaS being the most common model. Industries such as healthcare, finance, retail, and government are now running critical processes on SaaS platforms. This rapid growth makes SaaS Security & Compliance in Canada a top priority, as sensitive data and operational workflows need robust protection to maintain regulatory compliance and customer trust.
But this growth brings new challenges. Canadian businesses face rising risks of data breaches, ransomware attacks, and compliance violations. According to the Canadian Centre for Cyber Security, 70% of large organizations reported at least one cybersecurity incident in the past two years, many linked to cloud applications. These incidents don’t just cause operational disruption: they can also lead to PIPEDA fines, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust. For Canadian organizations, SaaS security is essential to protect sensitive data, maintain compliance, and support growth. With apps used across multiple teams, a robust SaaS management platform in Canada centralizes visibility, monitors vendor compliance, and reduces hidden risks, as platforms like Clarro make oversight simple and secure.
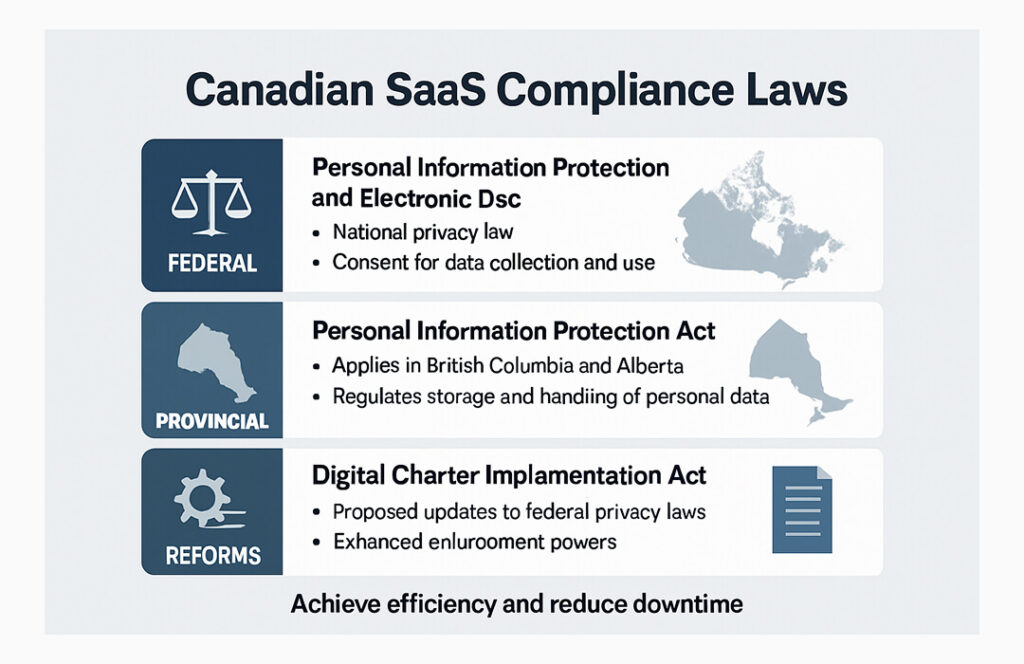
Canadian SaaS Compliance Laws You Can’t Ignore
Canadian businesses leveraging SaaS platforms must navigate a complex landscape of privacy and data protection laws. Compliance isn’t optional: it’s essential for safeguarding customer trust and avoiding significant penalties. Implementing a reliable SaaS security solution helps businesses manage sensitive data, meet federal and provincial requirements, and maintain regulatory compliance
1. PIPEDA – Canada’s Federal Privacy Law
The Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) is Canada’s federal privacy law that governs how private-sector organizations collect, use, and disclose personal information during commercial activities. It applies to all organizations across Canada, except in provinces that have their own substantially similar laws. Under PIPEDA, organizations must obtain consent when collecting personal information, protect the information with appropriate safeguards, and be transparent about their data practices.
Key requirements include:
- Consent: Organizations must obtain an individual’s consent when collecting, using, or disclosing personal information.
- Transparency: Organizations must inform individuals about the purposes for which their personal information is being collected.
- Access and Correction: Individuals have the right to access their personal information and request corrections.
- Safeguards: Organizations must protect personal information with security safeguards appropriate to the sensitivity of the information.
Non-compliance with PIPEDA can result in investigations by the Privacy Commissioner and potential fines.
2. Provincial Privacy Laws
In addition to PIPEDA, certain provinces have enacted their own privacy laws that apply to personal information collected within their jurisdictions:
- Quebec: The Act respecting the protection of personal information in the private sector governs the collection, use, and disclosure of personal information by private-sector organizations in Quebec. It includes provisions similar to PIPEDA but also introduces additional requirements, such as the obligation to notify the Commission d’accès à l’information of any personal data breach.
- British Columbia and Alberta: Both provinces have their own private-sector privacy laws: the Personal Information Protection Act (PIPA) in British Columbia and the Personal Information Protection Act (PIPA) in Alberta. These laws are deemed substantially similar to PIPEDA and apply to organizations collecting, using, or disclosing personal information in the course of commercial activities within the respective provinces.
Implementing a reliable SaaS Security Canada solution helps businesses manage sensitive data, meet federal and provincial requirements, and maintain regulatory compliance. Platforms like Clarro make oversight simple and secure, helping Canadian organizations stay audit-ready while reducing risks associated with shadow IT and unauthorized applications.
3. Bill C-27 / CPPA – Proposed Federal Privacy Reform
Bill C-27, introduced in 2022, aims to modernize Canada’s federal privacy framework by replacing PIPEDA with the Consumer Privacy Protection Act (CPPA). The CPPA introduces several key changes:
- Enhanced Consent Requirements: Organizations would be required to obtain clear and meaningful consent for the collection, use, and disclosure of personal information.
- Data Portability: Individuals would have the right to request the transfer of their personal information to another organization.
- Stronger Enforcement: The CPPA would grant the Privacy Commissioner the authority to issue orders and impose fines for non-compliance.
As of early 2025, Bill C-27 has not yet been enacted, but organizations should prepare for its potential implementation by reviewing their data practices and ensuring they align with the proposed requirements.
SaaS Security Risks Facing Canadian Companies
As Canadian businesses increasingly adopt SaaS solutions, they face several security challenges that can jeopardize compliance and data integrity. Understanding these risks is crucial for maintaining operational security and meeting regulatory requirements.
1. Shadow IT & Unauthorized Applications
Shadow IT occurs when employees use applications and services without IT approval. This can create significant security vulnerabilities:
- Lack of Visibility: IT teams may be unaware of which applications are in use, making monitoring and protection difficult.
- Compliance Risks: Unauthorized apps may not meet Canadian privacy regulations, potentially leading to legal issues.
- Data Breaches: Apps outside the organization’s security protocols can increase the risk of data leaks.
A study by Grip Security found that 43% of data breaches involve shadow IT, highlighting the importance of tracking and managing all SaaS applications.
2. Misconfigured Access Permissions
Improper access controls can expose sensitive data to unauthorized individuals:
- Excessive Permissions: Users having more access than necessary increases the risk of accidental or malicious exposure.
- Inconsistent Policies: Without standardized access protocols, some apps may have weak security.
- Insider Threats: Employees with unnecessary access can compromise data intentionally or unintentionally.
Regular audits and role-based access control are essential to minimize these risks.
3. Data Residency Challenges
Canadian laws require that sensitive data be stored and processed within Canada unless explicit consent is obtained:
- PIPEDA Compliance: The Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act mandates proper handling of personal data.
- Provincial Regulations: Provinces like British Columbia and Alberta have additional rules for data protection.
- International Data Transfers: Storing data in countries with weaker privacy laws can create legal and compliance risks.
Platforms like Clarro help Canadian businesses centralize SaaS tracking, enforce access controls, and ensure data residency compliance, reducing risks associated with shadow IT, misconfigured permissions, and cross-border data challenges.

Common Compliance Challenges for Canadian SMBs & Startups
Small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) in Canada are rapidly adopting SaaS solutions to streamline operations, manage customer relationships, and enhance productivity. However, SaaS compliance can be a complex challenge for SMBs, which often lack dedicated IT and legal teams.
1. Managing Multiple Vendor Certifications
Canadian businesses often use multiple SaaS providers for HR, finance, sales, and collaboration. Each vendor may hold different security certifications, such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, and PIPEDA compliance. Tracking and validating these certifications manually can be time-consuming, and missing updates may expose the organization to compliance gaps.
2. Staying Updated with Evolving Canadian Privacy Laws
Privacy regulations in Canada are rapidly evolving. SMBs must keep pace with federal and provincial laws, including:
- PIPEDA – Governs how personal information is collected, used, and disclosed.
- Provincial PIPAs – British Columbia, Alberta, and Quebec have additional regulations.
- Upcoming Bill C-27 / CPPA – Introduces stronger consumer privacy rights and stricter compliance requirements.
Without a centralized compliance strategy, SMBs may struggle to ensure their SaaS tools meet the latest legal requirements, increasing the risk of fines and reputational damage.
3. Lack of Visibility into Renewals, Risks, and Unauthorized SaaS Usage
Many SMBs lack a centralized view of all SaaS subscriptions, creating blind spots:
- Renewal Management: Missing renewal dates can lead to lapses in contracts or vendor compliance.
- Risk Exposure: Unauthorized apps or misconfigured permissions increase data breach risks.
- Audit Readiness: Preparing for compliance audits can be overwhelming without automated tracking tools.
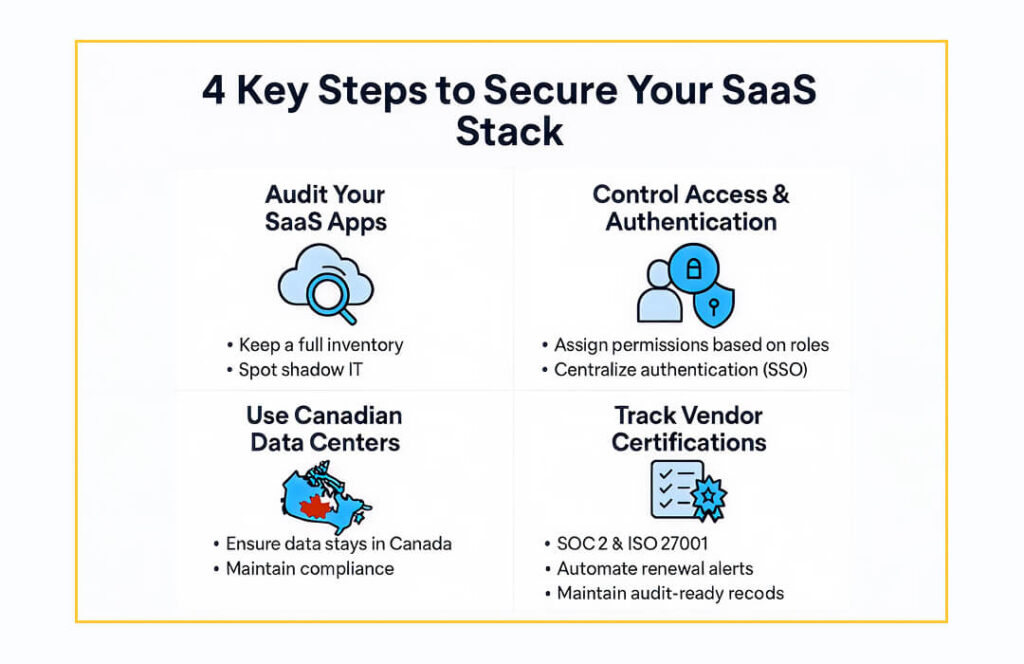
Best Practices for SaaS Security & Compliance
As Canadian businesses increasingly adopt Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions, ensuring robust security and compliance becomes paramount. Implementing best practices not only mitigates risks but also fosters trust with customers and partners.
1. Audit Your SaaS Stack Regularly
Regular audits are crucial for identifying and managing risks associated with SaaS applications:
- Comprehensive Inventory: Maintain an up-to-date list of all SaaS applications in use, including shadow IT instances.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate each application’s compliance with Canadian regulations, such as PIPEDA.
- Usage Monitoring: Track application usage patterns to identify unauthorized or underutilized tools.
According to the Cloud Security Alliance, regular audits help in identifying misconfigurations and unauthorized applications, which are common vectors for security breaches
2. Enforce Role-Based Access & Single Sign-On (SSO)
Implementing strict access controls reduces the risk of unauthorized data access:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign permissions based on user roles to ensure individuals have access only to necessary data.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Centralize authentication to streamline user access and enhance security.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Add an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of verification.
The Canadian Centre for Cyber Security emphasizes the importance of implementing least privilege access controls and multi-factor authentication to protect sensitive information
3. Choose SaaS with Canadian Data Centers
Data residency is a critical factor for compliance with Canadian privacy laws:
- Local Data Storage: Opt for SaaS providers that store data within Canada to comply with PIPEDA and provincial regulations.
- Data Sovereignty: Ensure that data handling practices align with Canadian legal requirements.
- Vendor Transparency: Verify that providers disclose data storage locations and compliance certifications.
Selecting SaaS providers with Canadian data centers helps mitigate risks associated with cross-border data transfers and ensures compliance with local laws.
4. Monitor Vendor Certifications & Renewals
Keeping track of vendor certifications ensures ongoing compliance:
- Certification Tracking: Regularly verify that vendors maintain relevant certifications, such as SOC 2 and ISO 27001.
- Renewal Management: Monitor certification expiration dates and initiate renewal processes in advance. Using compliance automation for startups can simplify these tasks, reduce manual effort, and ensure continuous adherence to regulations.
- Audit Trails: Maintain records of vendor certifications and compliance status for audit purposes.
Proactively managing vendor certifications helps in maintaining a secure and compliant SaaS environment.
The Future of SaaS Security in Canada
Canada’s SaaS compliance landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by evolving privacy laws, increasing demand for local cloud infrastructure, and the rise of automation in compliance processes.
1. Bill C-27 (CPPA): Redefining Consumer Data Rights
Bill C-27, known as the Consumer Privacy Protection Act (CPPA), aims to modernize Canada’s privacy framework by:
- Enhancing Consent Requirements: Strengthening how organizations obtain and manage consent for data collection.
- Introducing Algorithmic Transparency: Mandating organizations to disclose the logic behind automated decision-making processes.
- Establishing Data Portability: Allowing individuals to transfer their personal data between service providers.
These changes necessitate that Canadian SaaS providers implement robust data governance and transparency measures to comply with the new regulations.
2. Surge in Demand for Canadian Cloud and Sovereign Hosting
The Canadian cloud computing market is experiencing rapid growth, with projections indicating a significant increase in revenue by 2030. This surge is driven by:
- Data Residency Requirements: Organizations seeking to store data within Canada to comply with PIPEDA and provincial privacy laws.
- Local Data Centers: The establishment of new data centers by major providers, such as IBM’s expansion in Quebec, is expected to meet the growing demand for local cloud services.
This trend underscores the importance of selecting SaaS providers with Canadian data centers to ensure compliance and data sovereignty.
3. Transition from Manual Audits to Compliance Automation
The complexity of managing SaaS compliance is leading to a shift towards automation:
- Automated Compliance Tools: Platforms are integrating AI and machine learning to streamline compliance processes, reducing manual effort and increasing accuracy.
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time tracking of vendor certifications and data residency status to maintain up-to-date compliance.
- Scalability: Automation enables organizations to manage compliance across a growing number of SaaS applications efficiently.
Embracing compliance automation is becoming essential for Canadian businesses to stay ahead in a rapidly changing regulatory environment.
SaaS Security Checklist for Canadian Businesses
As Canadian businesses increasingly rely on SaaS solutions for operations, HR, finance, and customer management, maintaining robust security and compliance is crucial. Implementing a structured checklist ensures data protection, regulatory adherence, and operational efficiency. Here’s a detailed guide to safeguard your SaaS ecosystem:
1. Audit All SaaS Tools in Use
- Maintain a Central Inventory: Keep a comprehensive list of all SaaS applications in use, including department-level tools and any shadow IT. This provides full visibility into your organization’s software ecosystem.
- Identify Shadow IT: Unapproved apps can introduce hidden security risks and compliance gaps. Regular discovery and monitoring help prevent data breaches.
- Assess Usage and Redundancy: Determine which applications are actively used and remove redundant or obsolete tools to minimize attack surfaces.
Real-World Insight: A report by Gartner found that 30–40% of SaaS applications in an enterprise environment often go unmanaged, increasing security risk.
2. Verify Vendor Compliance Certifications
- SOC 2 & ISO 27001: Confirm that vendors adhere to international standards for data security and management.
- PIPEDA & CPPA Compliance: Ensure vendors comply with Canadian privacy regulations and upcoming laws like Bill C-27.
- Centralized Monitoring: Using a SaaS compliance dashboard helps track all vendor certifications in one place, making audits simpler and reducing manual effort.
- Keep Documentation Ready: Maintain records of vendor certifications and compliance reports to simplify audits and demonstrate due diligence.
Why It Matters: According to the Canadian Centre for Cyber Security, compliance verification reduces legal exposure and protects customer trust.
3. Ensure Data Residency in Canada
- Canadian Data Centers: Prioritize SaaS providers that store and process sensitive data within Canadian borders.
- Data Sovereignty: Local storage protects data from foreign jurisdiction risks and aligns with federal and provincial privacy laws.
- Vendor Transparency: Verify that providers clearly document where data is stored, how it is managed, and who has access.
Real Examples: Microsoft, AWS, and Google Cloud offer Canadian-based regions for PIPEDA compliance. Similarly, Clarro stores all SaaS usage data and compliance records in Canadian data centers, ensuring visibility and regulatory peace of mind.
4. Automate Vendor Monitoring & Renewals
- Track Certifications Continuously: Use automated tools to monitor SOC 2, ISO 27001, and PIPEDA/CPPA certifications.
- Receive Renewal Alerts: Ensure certificates and vendor agreements are up-to-date to avoid compliance gaps.
- Simplify Audits: Automation creates clear logs and records for regulatory inspections.
Industry Insight: Automated compliance monitoring reduces manual work by up to 60%, according to a report by ISACA, enabling teams to focus on strategic security initiatives.
5. Train Employees on SaaS Security Basics
- Security Awareness Programs: Conduct regular training sessions covering phishing, password hygiene, and safe SaaS usage.
- Role-Based Access Understanding: Educate employees on access rights, ensuring least-privilege principles are followed.
- Policy Updates & Communication: Keep staff informed about new compliance regulations, data handling procedures, and organizational policies.
Best Practice: The Canadian Centre for Cyber Security emphasizes that human error accounts for over 80% of cybersecurity incidents; employee training is therefore a critical defense.
Read More: Top 7 Challenges to Tackle in Custom Software Development
Clarro: Your Partner in SaaS Security & Compliance
For Canadian businesses, managing SaaS security and compliance can be complex, especially with multiple vendors, evolving regulations, and sensitive data to protect. Clarro offers a centralized, automated platform that simplifies SaaS management, making security and compliance easier, faster, and more reliable.
Key Features of Clarro
- Compliance Dashboard – Track all your SaaS vendors’ SOC 2, ISO 27001, and PIPEDA/CPPA certifications in one place. This ensures you are always audit-ready and compliant with Canadian privacy laws.
- Shadow IT Detection – Identify unauthorized SaaS applications in use across your organization. Reduce blind spots, prevent compliance gaps, and maintain full visibility over all software adoption.
- Automated Reports – Generate audit-ready reports with just a few clicks. Clarro automates compliance reporting for internal reviews and regulatory checks, saving your team hours of manual work.
- Renewal & Certification Monitoring – Never miss a vendor certification renewal or compliance expiration. Clarro provides automated vendor compliance monitoring, sending real-time alerts to keep your organization proactive and audit-ready. This ensures continuous oversight of all SaaS vendors and reduces the risk of compliance gaps.
Why Canadian Businesses Trust Clarro
Clarro is designed specifically for Canadian organizations that need reliable SaaS governance. With Canadian data residency, full vendor visibility, and automated compliance monitoring, businesses can confidently scale their SaaS usage while meeting federal and provincial regulations.
Clarro Advantage: By centralizing SaaS security canada and compliance, Clarro turns complex processes into simple, automated workflows, helping Canadian businesses reduce risk, save time, and focus on growth.
Final Thoughts
SaaS drives growth for Canadian businesses, but without proper SaaS Security Canada, it can pose serious risks, including data breaches and regulatory fines. By centralizing SaaS management, monitoring vendor compliance, detecting shadow IT, and generating audit-ready reports, organizations can ensure robust SaaS Security in Canada while focusing on scaling operations efficiently and securely.
Clarro centralizes SaaS management, monitors vendor compliance, detects shadow IT, and generates audit-ready reports, helping Canadian businesses reduce risks and focus on growth.

(FAQs)
1. What is PIPEDA compliance for SaaS?
The Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) requires Canadian businesses to obtain consent before collecting personal data, secure that data from unauthorized access, and ensure that any third-party SaaS vendors handling the data comply with the same privacy and security standards. Non-compliance can result in fines and reputational damage.
2. What is the CPPA (Bill C-27) and how does it impact SaaS?
The Consumer Privacy Protection Act (CPPA), also known as Bill C-27, will replace PIPEDA with stricter privacy rules and higher penalties for violations. SaaS vendors serving Canadian businesses must adopt enhanced privacy measures, including stronger data handling practices, breach reporting, and robust consent management. Organizations will need to ensure all SaaS providers comply to avoid legal and financial risks.
3. Why is data residency important in Canada?
Canadian laws require that sensitive personal and business data be stored in Canadian data centers unless explicit consent for cross-border transfer is obtained. Ensuring data residency in Canada helps businesses comply with PIPEDA and provincial privacy regulations (e.g., Quebec, Alberta, BC) and reduces the risk of legal or regulatory penalties.
4. How can SMBs manage SaaS compliance affordably?
Small and mid-sized businesses can streamline compliance by using SaaS management platforms like Clarro, which provide:
> Centralized tracking of all SaaS applications
> Automated monitoring of vendor certifications and renewals
> Audit-ready reporting for PIPEDA/CPPA compliance
This reduces the need for large compliance teams while ensuring security and regulatory adherence.